
Call to Negro America to March on Washington for Jobs and Equal Participation in National Defense, 1941
Primary Document by A. Philip Randolph
In 1941, A. Philip Randolph, the president of the Brotherhood of Sleeping Car Porters, issued a call to African Americans to fight the unjust conditions in the workforce with a March on Washington for Jobs and Freedom. The threatened mass protest forced President Franklin Roosevelt to sign Executive Order 8802 in June 1941, banning discrimination in the federal government and the defense industry. On June 28, A. Philip Randolph postponed the march.

1963 March on Washington for Jobs and Freedom Statement and Demands
By heads of ten organizations calling for the March of August 28, 1963
The 1963 March on Washington had a list of ten demands. Half of the demands were not about integration or education – they were about labor and economic rights.
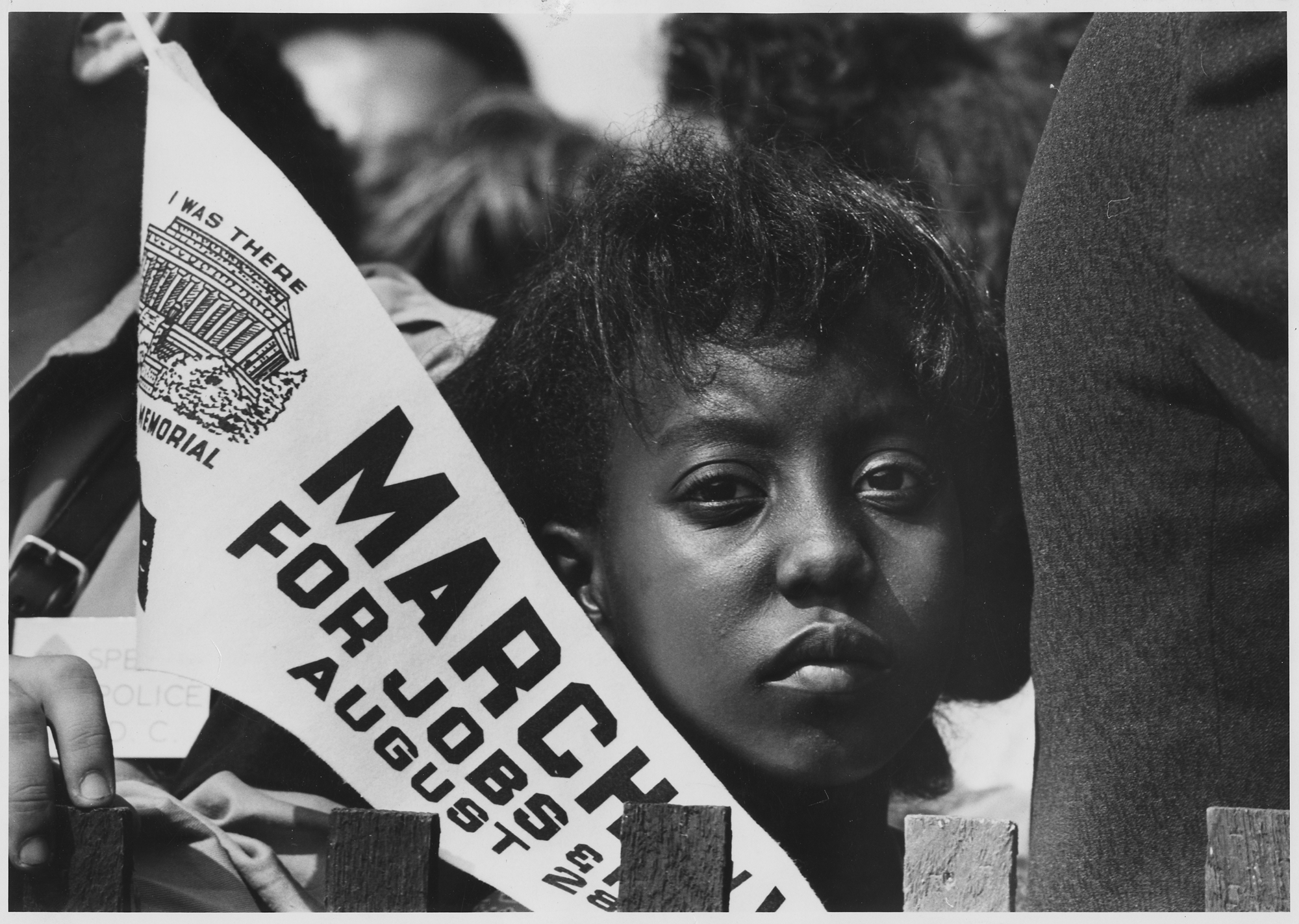
Claiming and Teaching the 1963 March on Washington
Reading by Bill Fletcher Jr.
The March on Washington did not begin as a classic civil rights march. It is barely remembered that the March on Washington was for freedom AND jobs, or that the march was initiated by black labor leaders.

At the River I Stand: The 1968 Memphis Sanitation Workers Strike and the Assassination of Martin Luther King Jr.
Reading by California Newsreel
The documentary film At the River I Stand skillfully reconstructs the two eventful months that transformed a strike by Memphis sanitation workers into a national conflagration, and disentangles the complex historical forces that came together with the inevitability of tragedy at the death of Martin Luther King Jr.

Our House Divided: What U.S. Schools Don’t Teach About U.S.-Style Apartheid
Reading by Richard Rothstein
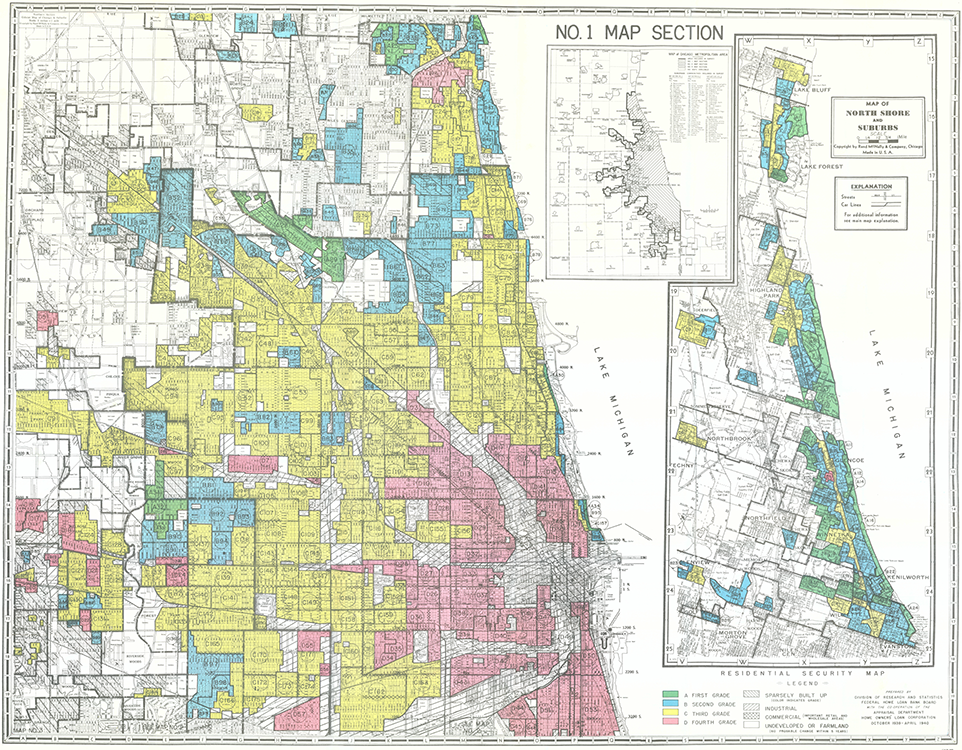
The widespread belief that our continued residential racial segregation, North and South, is “de facto,” not the result of explicit government policy but instead the consequence of private prejudice, economic inequality, and personal choice to self-segregate is false. In truth, our major metropolitan areas were segregated by government action.
The Case for Reparations
Interview of Ta-Nehisi Coates by Audi Cornish
Ta-Nehisi Coates describes how the legacy of slavery extends to geographical and governmental policies in the United States and calls for a "collective introspection" on reparations.

The Unknown Origins of the March on Washington: Civil Rights Politics and the Black Working Class
Reading by William P. Jones
“The very decade which has witnessed the decline of legal Jim Crow has also seen the rise of de facto segregation in our most fundamental socioeconomic institutions,” veteran civil rights activist Bayard Rustin wrote in 1965. The March on Washington addressed the economic crisis facing working-class African Americans more effectively than any other mobilization since the Second World War.
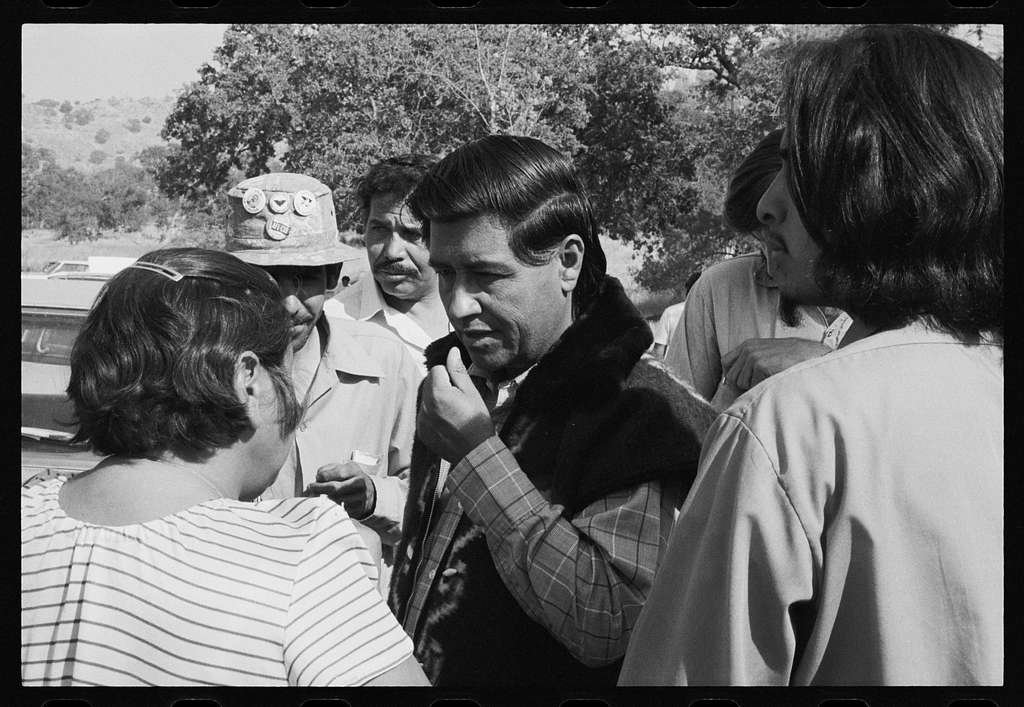

César Chávez on How It Began
Interview with César Chávez by Luis Torres
In an interview just before his death in 1993, César Chávez related the story of how the fledgling National Farm Worker Association (NFWA) union became involved with Filipino workers belonging to the Agricultural Workers Organizing Committee and the strike against major grape growers.

A Brief History of Black Cooperatives in the United States
Interview of Dr. Jessica Gordon Nembhard By Mira Luna
For as long as there have been Africans in America, there have been examples of Black social, cultural and economic solidarity. Often formed in response to systemic exclusion and economic stagnation, examples range from mutual aid networks, to freedom farms and grocery cooperatives.

The Great Land Robbery: The shameful story of how 1 million black families have been ripped from their farms
Reading by Vann R. Newkirk II
A war waged by deed of title has dispossessed 98 percent of black agricultural landowners in America. Through a variety of means—sometimes legal, often coercive, in many cases legal and coercive, occasionally violent—farmland owned by black people came into the hands of white people. It was aggregated into larger holdings, then aggregated again, eventually attracting the interest of Wall Street.

African Americans Have Lost Untold Acres of Land Over the Last Century: An obscure legal loophole is often to blame
Reading by Leah Douglas
In the years following the Civil War, formerly enslaved people and their descendants accumulated roughly 15 million acres of land, roughly 14 percent of all farms in the U.S. Today, African Americans compose less than 2 percent of the nation’s farmers and 1 percent of rural landowners.
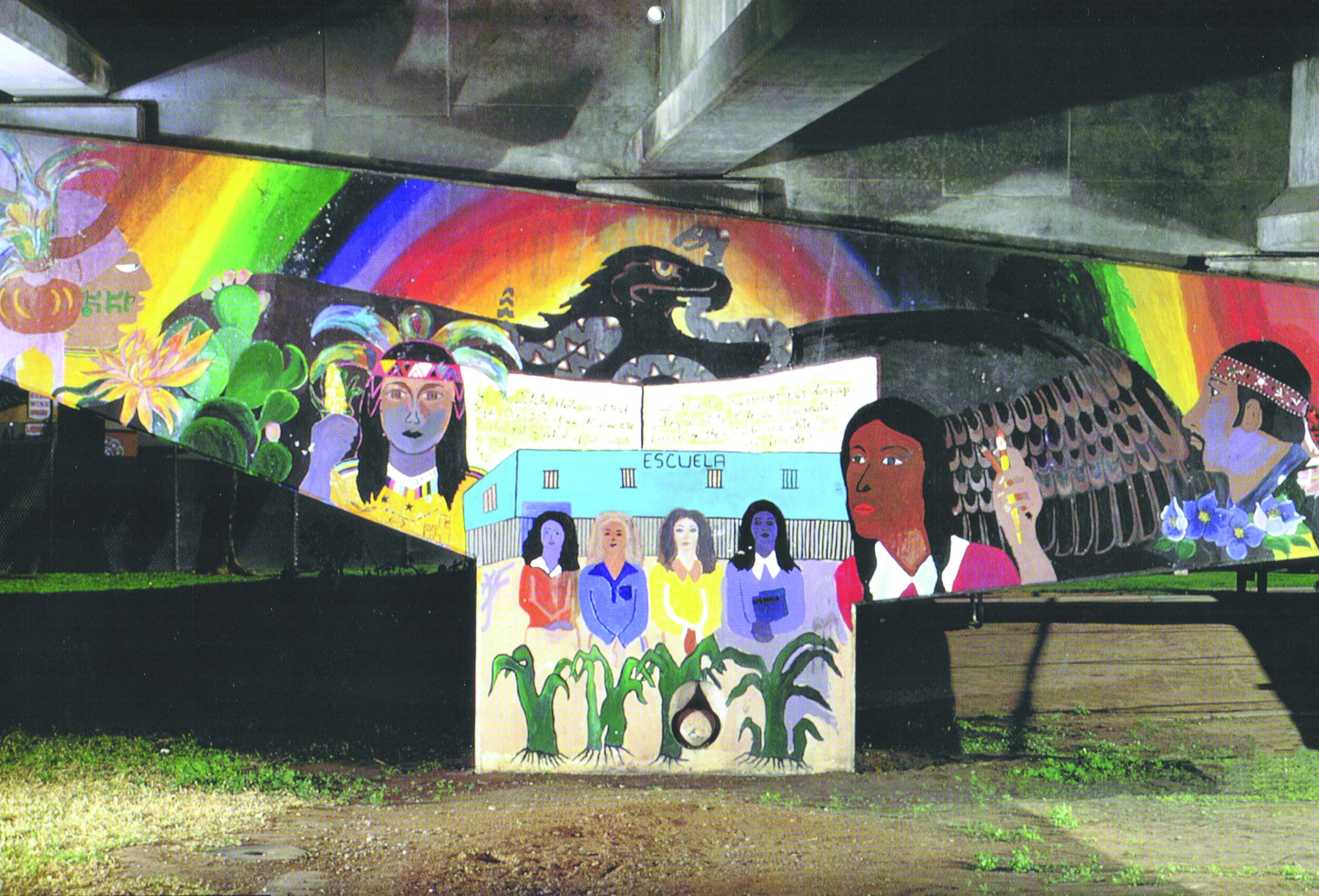

Murals: Redefining Culture, Reclaiming Identity
Reading by Eva Sperling Cockcroft and Holly Barnet-Sanchez
A powerful essay on the connections among art, identity, and activism excerpted from the introduction to Signs from the Heart: California Chicano Murals.
